Given a n-ary tree, find its maximum depth.
The maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
Nary-Tree input serialization is represented in their level order traversal, each group of children is separated by the null value (See examples).
Example 1:

Input: root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
Output: 3
Example 2:
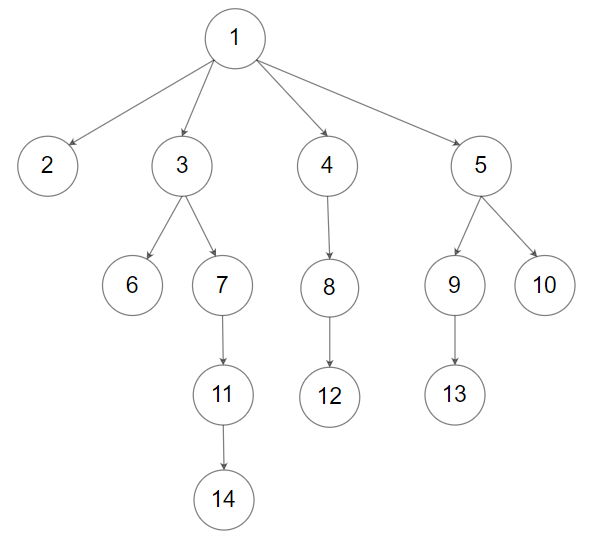
Input: root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
Output: 5
Constraints:
- The total number of nodes is in the range [0, 104].
- The depth of the n-ary tree is less than or equal to 1000.
제목에서도 볼 수 있듯이 Recursive 또는 Stack/Queue + while문의 기운이 강하게 맴도는 녀석이다.
두려워 말고 진전해보자.
1. Python
Easy 난이도 이긴 하지만 ㅎㅎ...
일단 장하게도 별 도움 없이 Recursive하게 문제를 풀어냈다.
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val: Optional[int] = None, children: Optional[List['Node']] = None):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: 'Node') -> int:
# Make a stack of nodes
# Increase cnt + 1 whenever it calls children
# No.. go recursive
if not root : return 0
elif not root.children : return 1
lst = deque()
def helper(node,cnt):
cnt+=1
if not node.children :
lst.append(cnt)
return
else :
n = len(node.children)
for j in range(n):
helper(node.children[j],cnt)
for i in range(len(root.children)):
cnt = 1
helper(root.children[i],cnt)
return max(lst)아직 서툴러서 코드가 좀 조잡하다.
분명 같은 Recursive라도 좀 더 깔끔하게 코딩하는 방법이 있을 거 같기도 하다.
원래는 Stack, Queue를 써서 풀려고 했는데 머리가 굳어서 그렇게 할 수가 없었다..ㅠ
깔끔한 Recursive는 아래와 같다.
C를 이용해서 표현해 보았다
2. C
// Definition for a Node.
struct Node {
int val;
int numChildren;
struct Node** children;
};
int max(int a, int b){
return a >= b ? a : b;
}
int maxDepth(struct Node* root) {
if(!root) return 0;
int cnt = 0;
for(int i=0;i<root->numChildren;i++){
cnt = max(cnt,maxDepth(root->children[i]));
}
return cnt+1;
}
3. C++로는 Queue -> BFS , Stack -> DFS 모두를 해보자
3-1. Queue - BFS
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
// BFS with Queue
if(!root) return 0;
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
int cnt = 0;
while(!q.empty()){
int n = q.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
Node* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
for(auto x : curr->children) q.push(x);
}
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
};
3-2. Stack - DFS
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
int max_depth = 0;
if(!root) return max_depth;
stack<pair<Node*,int>> s;
s.push({root,1});
while(!s.empty()){
Node* curr = s.top().first;
int dept = s.top().second;
s.pop();
max_depth = max(max_depth,dept);
for(auto x : curr->children){
s.push({x,dept+1});
}
}
return max_depth;
}
};