https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-bst/description/
Given the root of a binary search tree, and an integer k, return the kth smallest value (1-indexed) of all the values of the nodes in the tree.
Example 1:
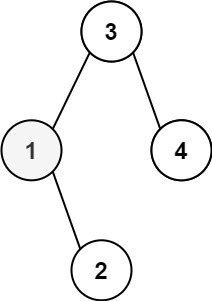
Input: root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1
Output: 1
Example 2:
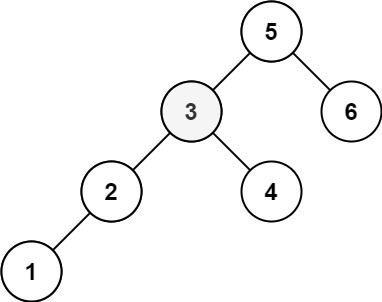
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3
Output: 3
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is n.
- 1 <= k <= n <= 104
- 0 <= Node.val <= 104
Follow up: If the BST is modified often (i.e., we can do insert and delete operations) and you need to find the kth smallest frequently, how would you optimize?
돌고 돌아 다시 leetcode BST문제이다.
In - order 느낌이 강하게 났다.
내가 이해한 Node Retrieval 문제는
Depth : Stack + while문 , 또는 Recursive
Breath : queue + while문이다.
1. Python
Stack + while문으로 풀어보았다.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def kthSmallest(self, root: TreeNode, k: int) -> int:
#Traversal - In-Order?
visited = []
s = deque([root])
while s:
curr = s[-1]
if curr.left and curr.left.val not in visited :
s.append(curr.left)
continue
else :
visited.append(curr.val)
s.pop()
if len(visited) == k : return visited[-1]
if curr.right:
s.append(curr.right)
|
위에 내가 푼 코드의 경우, GPT한테 개선점이 있는지 물어봤더니 visited라는 별도의 memory를 안 쓰고 푸는 방법을 알려주었다. 확실히 이렇게 하니까 가독성이 좀 더 좋긴 하다.. 아으
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def kthSmallest(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], k: int) -> int:
s = deque()
curr = root
cnt = 0
while s or curr :
while curr :
s.append(curr)
curr = curr.left
curr = s.pop()
cnt +=1
if cnt == k : return curr.val
curr = curr.right
2. C
이번엔 Recursive를 이용해서 풀어 본다.
// Definition for a binary tree node.
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
};
void helper(struct TreeNode* node, int* cnt, int* result){
if(!node) return;
helper(node->left,cnt,result);
(*cnt)--;
if(*cnt==0){
*result = node->val;
return;
}
helper(node->right,cnt,result);
}
int kthSmallest(struct TreeNode* root, int k) {
int result;
helper(root,&k,&result);
return result;
}
3.C++도 역시나 recursive하게!
// * Definition for a binary tree node.
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
void inorder(TreeNode* node, int& cnt, int& ans){
if(!node) return;
inorder(node->left,cnt,ans);
cnt--;
if(cnt==0){
ans = node->val;
return;
}
else inorder(node->right,cnt,ans);
}
int kthSmallest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
int ans;
inorder(root,k,ans);
return ans;
}
};
참고로, Tree의 Traversal 순서에 따른 코드는 아래와 같다.
|
트리 노드 구조체 정의
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
1. 전위 순회 (Pre-order Traversal)
void preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return;
// 현재 노드 방문
cout << root->val << " ";
// 왼쪽 자식 방문
preorderTraversal(root->left);
// 오른쪽 자식 방문
preorderTraversal(root->right);
}
2. 중위 순회 (In-order Traversal)
void inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return;
// 왼쪽 자식 방문
inorderTraversal(root->left);
// 현재 노드 방문
cout << root->val << " ";
// 오른쪽 자식 방문
inorderTraversal(root->right);
}
3. 후위 순회 (Post-order Traversal)
void postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return;
// 왼쪽 자식 방문
postorderTraversal(root->left);
// 오른쪽 자식 방문
postorderTraversal(root->right);
// 현재 노드 방문
cout << root->val << " ";
}
이상!
'Coding_Practice' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array2[Array,Binary Search] (2) | 2024.10.31 |
|---|---|
| Min Stack[Stack,Design] (0) | 2024.10.31 |
| MaxProfit(Given a log of stock prices compute the maximum possible earning) (4) | 2024.10.30 |
| Maximum Depth of N-ary Tree[Tree,Depth-First Search,Breadth-First Search] (1) | 2024.10.29 |
| Is Graph Bipartite?[Depth-First Search,Breadth-First Search,Union Find,Graph] (1) | 2024.10.28 |