C - 2개 / C++ - 2개 이렇게 총 4개의 코딩문제를 3시간에 거쳐서 풀어보았다.
문제는 Time / Space Complexcity를 크게 고려하지 않고, 정답만 도출되면 인정되는 부분이라 어거지로 코드를 짜서 답을 도출해내는 데에는 성공을 했으나..
앞으로 좀 더 효율적인 코딩을 하기 위해선 Coding Review정도는 하고 넘어가는 것이 좋을 거 같아 글을 적어본다.
문제의 출처도 제공되진 않지만, 시험이 끝나고 내가 스스로 복기 + 구글링/GPT를 이용해서 문제 출처를 추려내어 보았다.
1번 문제
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/42627
프로그래머스
SW개발자를 위한 평가, 교육, 채용까지 Total Solution을 제공하는 개발자 성장을 위한 베이스캠프
programmers.co.kr
문제 설명
하드디스크는 한 번에 하나의 작업만 수행할 수 있습니다. 디스크 컨트롤러를 구현하는 방법은 여러 가지가 있습니다. 이 문제에서는 우선순위 디스크 컨트롤러라는 가상의 장치를 이용한다고 가정합니다. 우선순위 디스크 컨트롤러는 다음과 같이 동작합니다.
- 어떤 작업 요청이 들어왔을 때 작업의 번호, 작업의 요청 시각, 작업의 소요 시간을 저장해 두는 대기 큐가 있습니다. 처음에 이 큐는 비어있습니다.
- 디스크 컨트롤러는 하드디스크가 작업을 하고 있지 않고 대기 큐가 비어있지 않다면 가장 우선순위가 높은 작업을 대기 큐에서 꺼내서 하드디스크에 그 작업을 시킵니다. 이때, 작업의 소요시간이 짧은 것, 작업의 요청 시각이 빠른 것, 작업의 번호가 작은 것 순으로 우선순위가 높습니다.
- 하드디스크는 작업을 한 번 시작하면 작업을 마칠 때까지 그 작업만 수행합니다.
- 하드디스크가 어떤 작업을 마치는 시점과 다른 작업 요청이 들어오는 시점이 겹친다면 하드디스크가 작업을 마치자마자 디스크 컨트롤러는 요청이 들어온 작업을 대기 큐에 저장한 뒤 우선순위가 높은 작업을 대기 큐에서 꺼내서 하드디스크에 그 작업을 시킵니다. 또, 하드디스크가 어떤 작업을 마치는 시점에 다른 작업이 들어오지 않더라도 그 작업을 마치자마자 또 다른 작업을 시작할 수 있습니다. 이 과정에서 걸리는 시간은 없다고 가정합니다.
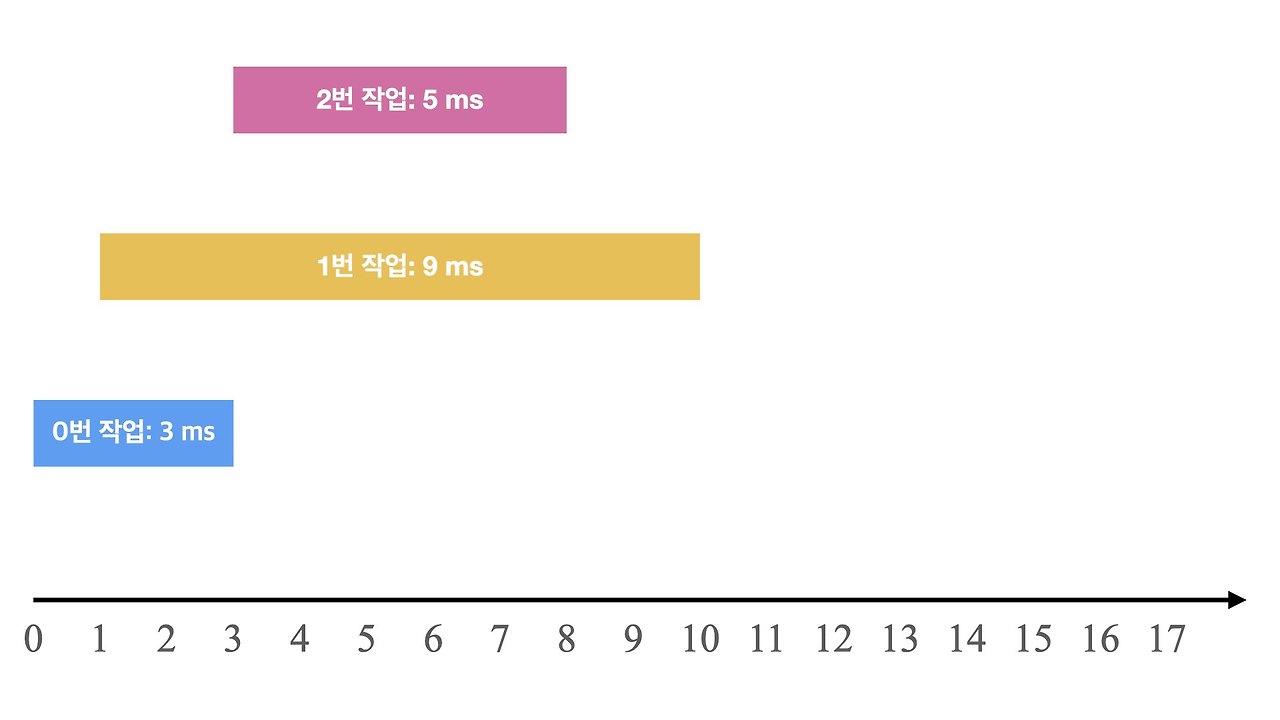
예를 들어
- 0ms 시점에 3ms가 소요되는 0번 작업 요청
- 1ms 시점에 9ms가 소요되는 1번 작업 요청
- 3ms 시점에 5ms가 소요되는 2번 작업 요청
와 같은 요청이 들어왔습니다. 이를 그림으로 표현하면 다음과 같습니다.
이 요청을 우선순위 디스크 컨트롤러가 처리하는 과정은 다음 표와 같습니다.
시점하드디스크대기 큐디스크 컨트롤러| 0ms | [] | ||
| 0ms | [[0번, 0ms, 3ms]] | 0번 작업 요청을 대기 큐에 저장 | |
| 0ms | 0번 작업 시작 | [] | 대기 큐에서 우선순위가 높은 0번 작업을 꺼내서 작업을 시킴 |
| 1ms | 0번 작업 중 | [[1번, 1ms, 9ms]] | 1번 작업 요청을 대기 큐에 저장 |
| 3ms | 0번 작업 완료 | [[1번, 1ms, 9ms]] | |
| 3ms | [[1번, 1ms, 9ms], [2번, 3ms, 5ms]] | 2번 작업 요청을 대기 큐에 저장 | |
| 3ms | 2번 작업 시작 | [[1번, 1ms, 9ms]] | 대기 큐에서 우선순위가 높은 2번 작업을 꺼내서 작업을 시킴 |
| 8ms | 2번 작업 완료 | [[1번, 1ms, 9ms]] | |
| 8ms | 1번 작업 시작 | [] | 대기 큐에서 우선순위가 높은 1번 작업을 꺼내서 작업을 시킴 |
| 17ms | 1번 작업 완료 | [] |
모든 요청 작업을 마쳤을 때 각 작업에 대한 반환 시간(turnaround time)은 작업 요청부터 종료까지 걸린 시간으로 정의합니다. 위의 우선순위 디스크 컨트롤러가 처리한 각 작업의 반환 시간은 다음 그림, 표와 같습니다.
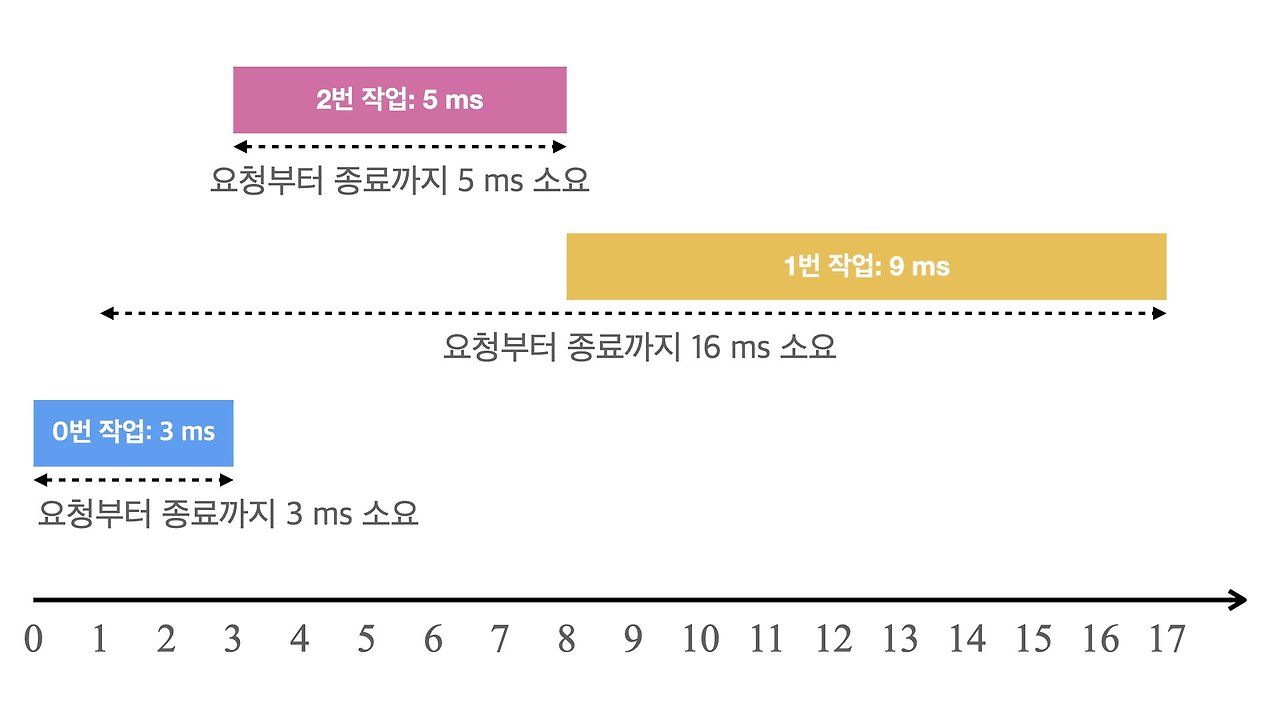
| 0번 | 0ms | 3ms | 3ms(= 3ms - 0ms) |
| 1번 | 1ms | 17ms | 16ms(= 17ms - 1ms) |
| 2번 | 3ms | 8ms | 5ms(= 8ms - 3ms) |
우선순위 디스크 컨트롤러에서 모든 요청 작업의 반환 시간의 평균은 8ms(= (3ms + 16ms + 5ms) / 3)가 됩니다.
각 작업에 대해 [작업이 요청되는 시점, 작업의 소요시간]을 담은 2차원 정수 배열 jobs가 매개변수로 주어질 때, 우선순위 디스크 컨트롤러가 이 작업을 처리했을 때 모든 요청 작업의 반환 시간의 평균의 정수부분을 return 하는 solution 함수를 작성해 주세요.
제한 사항
- 1 ≤ jobs의 길이 ≤ 500
- jobs[i]는 i번 작업에 대한 정보이고 [s, l] 형태입니다.
- s는 작업이 요청되는 시점이며 0 ≤ s ≤ 1,000입니다.
- l은 작업의 소요시간이며 1 ≤ l ≤ 1,000입니다.
입출력 예)
| [[0, 3], [1, 9], [3, 5]] | 8 |
처음에 내가 짠 코드는 아래와 같다.
굉장히 난잡하게 짰다 ㅎㅎ;;
struct CompareNode {
bool operator()(vector<int> a, vector<int> b) {
return a[1] > b[1]; // Min-heap based on R-value
}
};
int function1(vector<vector<int>> jobs) {
priority_queue<vector<int>, vector<vector<int>>, CompareNode> minHeap;
int n = jobs.size();
if(n==0) return 0;
if(n==1) return jobs[0][1];
int idx = 0;
int ans = 0;
sort(jobs.begin(),jobs.end()); // jobs를 request time 기준으로 오름차순 정렬
int curr_time = jobs[0][0]; // current time
while(idx!=n){
// 추잡한 방법으로 이미 Heap에 있는 놈들 체크함.. 이게 결국 맞긴 한데 더 효율적인 방법이 있는지 확인!
priority_queue<vector<int>, vector<vector<int>>, CompareNode> check;
check = minHeap;
vector<vector<int>> check2;
for(int j=0;j<check.size();j++){
check2.push_back(check.top());
check.pop();
}
for(const auto x : jobs){
auto it1 = find(check2.begin(),check2.end(),x);
if(it1!=check2.end()) continue;
if(x[0]<=curr_time){
minHeap.push(x);
}
}
// 현재 가장 우선순위로 실행될 녀석
vector<int> curr = minHeap.top();
minHeap.pop();
curr_time += curr[1]; // curr_time update
ans += (curr_time - curr[0]); // 소요시간 update
idx++;
//erase it
auto it2 = find(jobs.begin(),jobs.end(),curr);
jobs.erase(it2);
}
int result = ans/n;
return result;
}
문제에 있어서 효율성과 코드 가독성을 좀 더 개선해보자.
일단 while문 內 check / check2를 사용한 중복검사가 좀 비효율적이란 생각이 들었따.
그리고 jobs를 순회하면서 find + erase 하는 것도 좀 짜치긴하다.
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct CompareNode {
bool operator()(vector<int> a, vector<int> b) {
return a[1] > b[1]; // Min-heap based on job duration
}
};
int function1(vector<vector<int>> jobs) {
// Step 1: Sort jobs by request time
sort(jobs.begin(), jobs.end());
priority_queue<vector<int>, vector<vector<int>>, CompareNode> minHeap;
int n = jobs.size();
int curr_time = 0, idx = 0, total_time = 0;
// Step 2: Process jobs
while (idx < n || !minHeap.empty()) {
// Push all jobs that can be processed at the current time
while (idx < n && jobs[idx][0] <= curr_time) {
minHeap.push(jobs[idx]);
idx++;
}
if (!minHeap.empty()) {
// Process the job with the shortest duration
vector<int> job = minHeap.top();
minHeap.pop();
curr_time += job[1]; // Update current time
total_time += (curr_time - job[0]); // Total waiting time
} else {
// If no jobs are available, move the time to the next job's request time
curr_time = jobs[idx][0];
}
}
return total_time / n; // Return average waiting time
}
이렇게 하면 while문의 공회전(?)을 막아 효율적인 코드를 짤 수 있다. idx를 통해서 jobs를 돌면 사실 중복 jobs 값을 heap에 집어넣을 수 없는데, 왜 시험장에선 그게 잘 떠오르지가 않아서 vector ,heap을 추가로 만들고 중복check를 하는 주접을 떨었나 싶다.. 근데 뭐.. 항상 느끼는건데 솔루션을 보고 문제를 풀면 다~쉽다!
2번 문제
는 회전초밥문제였는데, 그리 어렵진 않아서 SKIP
3번 문제
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/43238
프로그래머스
SW개발자를 위한 평가, 교육, 채용까지 Total Solution을 제공하는 개발자 성장을 위한 베이스캠프
programmers.co.kr
풀 때는 걍 for문 돌려서 풀었는데, 문제 카테고리를 보니까 이분탐색이다. Binary Search..
일단 내 첫 풀이는 아래와 같다. 계속 for문 while문이네 ㅎㅎ;; 민망하다. 아 참고로 이건 'C"로 푼 것
long long function3(int n, int times[], int size) {
//일단 time을 sorting한다 -> 필요 없다
// 0으로 이루어진 arr 초기화
int ans[size] = {0};
// for(int i=0;i<size;i++) ans[i]=0;
int cnt = 0;
while(cnt!=n){
int idx;
int target = INT_MAX;
for(int k=0;k<size;k++){
if(ans[k]+times[k]<target){
target = ans[k]+times[k];
idx = k;
}
}
cnt++;
ans[idx] += times[idx];
}
long long result = INT_MIN;
for(int j=0;j<size;j++){
if(ans[j]>result) result = ans[j];
}
return result;
}
본래 문제의 쟁점은 이진 탐색 활용이니까 Binary Search를 한 번 쓰는 법을 알아보자
하.. C로는 Binary Search도 좀 짜친다.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <limits.h>
long long count_people(int time_limit, int times[], int size) {
long long total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
total += time_limit / times[i];
}
return total;
}
long long function3(int n, int times[], int size) {
long long left = 1;
long long right = (long long)n * times[0]; // 가장 긴 시간으로 초기화
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
if (times[i] > right / n) right = (long long)n * times[i];
}
long long result = right;
while (left <= right) {
long long mid = (left + right) / 2;
long long people_processed = count_people(mid, times, size);
if (people_processed >= n) {
result = mid; // 가능한 최소 시간 갱신
right = mid - 1;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return result;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
if (argc < 3) {
printf("Usage: ./main n \"times\"\n");
return 1;
}
int n = atoi(argv[1]);
char* token;
int times[100]; // 최대 100개의 검사관
int size = 0;
token = strtok(argv[2], " ");
while (token != NULL) {
times[size++] = atoi(token);
token = strtok(NULL, " ");
}
long long result = function3(n, times, size);
printf("Minimum time: %lld\n", result);
return 0;
}
C++로 하면 추가적인 Function 구현 필요 없이 문제를 풀 수 있으니 아래를 참고헙시다.
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
long long solution(int n, vector<int> times) {
// 이진 탐색 범위를 설정
long long left = 1;
long long right = (long long)n * *max_element(times.begin(), times.end()); // 가장 긴 시간으로 초기화
long long answer = right;
while (left <= right) {
long long mid = (left + right) / 2;
long long people_processed = 0;
// mid 시간 안에 처리 가능한 사람의 수 계산
for (int time : times) {
people_processed += mid / time;
if (people_processed >= n) break; // 불필요한 계산을 줄이기 위해 조기 종료
}
if (people_processed >= n) {
// 더 짧은 시간에서 가능한지 확인
answer = mid;
right = mid - 1;
} else {
// 더 많은 시간이 필요
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return answer;
}
솔직히 코드를 봐도 잘 모르겄다.
뭔가 log 시간 complexity라 효율적일 거 같긴한데.. 몰겄다 ㅋㅋ;;
4번 문제
https://www.codewars.com/kata/5e1b37bcc5772a0028c50c5d?utm_source=chatgpt.com
Codewars - Achieve mastery through coding practice and developer mentorship
A coding practice website for all programming levels – Join a community of over 3 million developers and improve your coding skills in over 55 programming languages!
www.codewars.com
이건 또 무엇인가.. Leetcode Meeting room Reservation문제와 풀이가 같다.
그것을 참고하면 될듯..
근데 왜 이렇게 소프트웨어 플랫폼이 많은 것이냐~ 풀 문제가 끝이 없다 끝이 없어
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
/*
You work at a taxi central.
People contact you to order a taxi. they inform you of the time they want to be picked up and dropped off. A taxi is available to handle a new customer 1 time until after it has dropped off a previous customer. Given requests, what is the minimum number of taxis you need to service all requests?
*/
int function4(vector<pair<int, int>> &requests) {
// Fill this function
if(requests.empty()) return 0;
// int ans = 1;
int n = requests.size();
sort(requests.begin(),requests.end());
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> minheap;
minheap.push(requests[0].second);
for(int i=1;i<requests.size();i++){
if(requests[i].first>minheap.top()) minheap.pop();
minheap.push(requests[i].second);
}
return minheap.size();
}
// If you need to construct another functions, write and use here.
// However, you can not use those functions in main.cpp.
// Submit functions.hpp file.
// compile command: g++ -o main main.cpp
// execute command:
// ./main "1 4 2 6 5 9"재밌다 재밌어..