https://leetcode.com/problems/sort-list/description/
Given the head of a linked list, return the list after sorting it in ascending order.
Example 1:

Input: head = [4,2,1,3]
Output: [1,2,3,4]
Example 2:
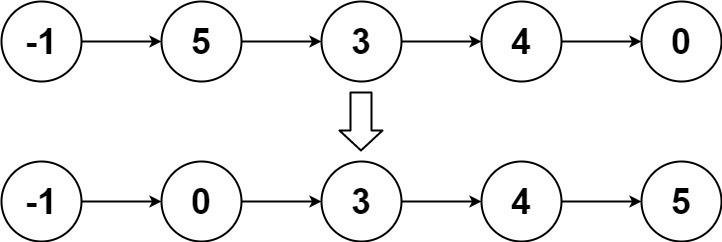
Input: head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
Output: [-1,0,3,4,5]
Example 3:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range [0, 5 * 104].
- -105 <= Node.val <= 105
Follow up: Can you sort the linked list in O(n logn) time and O(1) memory (i.e. constant space)?
사실 divide and conquer의 대표 예제는 Merge Sort라고 한다. 근데 이걸 대놓고 하는 거 보단, 이렇게 Linked List 녀석을 Merge sort 해보면 조금이라도 연습이 더 되지 않을까 해서 풀어보는 문제.............
1. Python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head or not head.next : return head
# Divide
slow = head
fast = head
slowest = head
while fast and fast.next:
slowest = slow
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
slowest.next = None
node_l = self.sortList(head)
node_r = self.sortList(slow)
# Conquer
def Merge(node1,node2):
dummy = ListNode(999)
curr = dummy
while node1 and node2:
if node1.val < node2.val:
curr.next = node1
node1 = node1.next
else :
curr.next = node2
node2 = node2.next
curr = curr.next
if node1:
curr.next = node1
else : curr.next = node2
return dummy.next
return Merge(node_l,node_r)우오아아아아앙ㅇ
어려운 문제 같은데 풀었다 ㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋ
물론 실락같은 GPT의 도움이 있긴했지만, 그래도 풀리니까 신기하다.
참.. 코딩은 하면 할수록 디버깅이 중요하다는 걸 깨닫는다.
분명 논리적으로 문제가 없어보이는데, 꼭 edge case에 걸리는 녀석들이 하나씩 있다
아으아!
GPT한테 내 코드를 좀 더 깔끔하게 다듬을 수 없냐고 했는데, slowest는 쓸 필요가 없다고 한다.
?? 그래놓고 코드 보니까 prev을 썼네. 그거나 그너나 이다 요놈아;;
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head or not head.next:
return head
# Divide
slow, fast = head, head
prev = None
while fast and fast.next:
prev = slow
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
prev.next = None # Split the list into two halves
# Recursively sort the two halves
left = self.sortList(head)
right = self.sortList(slow)
# Merge the sorted halves
return self.merge(left, right)
def merge(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
dummy = ListNode(0)
tail = dummy
while l1 and l2:
if l1.val < l2.val:
tail.next = l1
l1 = l1.next
else:
tail.next = l2
l2 = l2.next
tail = tail.next
tail.next = l1 if l1 else l2 # Attach remaining part of the list
return dummy.next
2. C++
돈돈~~하다
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head || !head->next) return head;
//Divide
ListNode* slowest = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next){
slowest = slow;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
slowest->next = nullptr;
ListNode* left = sortList(head);
ListNode* right = sortList(slow);
//Merge
return Merge(left,right);
}
ListNode* Merge(ListNode* l,ListNode* r){
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(999);
ListNode* tail = dummy;
while(l and r){
if(l->val < r->val){
tail->next = l;
l = l->next;
}else{
tail->next = r;
r = r->next;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = l ? l : r;
return dummy->next;
}
};
3. C
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* Merge(struct ListNode* l1,struct ListNode* r1){
struct ListNode* dummy = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode* temp = dummy;
while(l1 && r1){
if(l1->val < r1->val){
temp->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}else{
temp->next = r1;
r1 = r1->next;
}
temp = temp->next;
}
temp -> next = l1 ? l1 : r1;
struct ListNode* result = dummy->next;
free(dummy);
return result;
}
struct ListNode* sortList(struct ListNode* head) {
if(!head || !head->next) return head;
struct ListNode* slowest = head;
struct ListNode* slow = head;
struct ListNode* fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next){
slowest = slow;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
slowest->next = NULL;
struct ListNode* l1 = sortList(head);
struct ListNode* r1 = sortList(slow);
// Merge
return Merge(l1,r1);
}
물론 D and C 말고 최적화된 문제 풀이법이 많겠다만, 일단 요렇게만 적어보았다.
- E. O. D -