You are given a 0-indexed array of positive integers nums and a positive integer limit.
In one operation, you can choose any two indices i and j and swap nums[i] and nums[j] if |nums[i] - nums[j]| <= limit.
Return the lexicographically smallest array that can be obtained by performing the operation any number of times.
An array a is lexicographically smaller than an array b if in the first position where a and b differ, array a has an element that is less than the corresponding element in b. For example, the array [2,10,3] is lexicographically smaller than the array [10,2,3] because they differ at index 0 and 2 < 10.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,5,3,9,8], limit = 2
Output: [1,3,5,8,9]
Explanation: Apply the operation 2 times:
- Swap nums[1] with nums[2]. The array becomes [1,3,5,9,8]
- Swap nums[3] with nums[4]. The array becomes [1,3,5,8,9]
We cannot obtain a lexicographically smaller array by applying any more operations.
Note that it may be possible to get the same result by doing different operations.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,7,6,18,2,1], limit = 3
Output: [1,6,7,18,1,2]
Explanation: Apply the operation 3 times:
- Swap nums[1] with nums[2]. The array becomes [1,6,7,18,2,1]
- Swap nums[0] with nums[4]. The array becomes [2,6,7,18,1,1]
- Swap nums[0] with nums[5]. The array becomes [1,6,7,18,1,2]
We cannot obtain a lexicographically smaller array by applying any more operations.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,7,28,19,10], limit = 3
Output: [1,7,28,19,10]
Explanation: [1,7,28,19,10] is the lexicographically smallest array we can obtain because we cannot apply the operation on any two indices.
Constraints:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 105
- 1 <= nums[i] <= 109
- 1 <= limit <= 109
간만에 돌아온 Daily code다
머리에 불을 좀 지펴보자..!
1. Python
또 Rough 하게 풀었더니, 답이 안 나오는 case가 발생한다 -_-
일단, 망친 답안 하나
class Solution:
def lexicographicallySmallestArray(self, nums: List[int], limit: int) -> List[int]:
n = len(nums)
for i in range(n):
smallest = i
for j in range(i+1,n):
if nums[j] < nums[i] <= nums[j] + limit :
if nums[smallest] > nums[j] : smallest = j
nums[i] , nums[smallest] = nums[smallest] , nums[i]
return nums
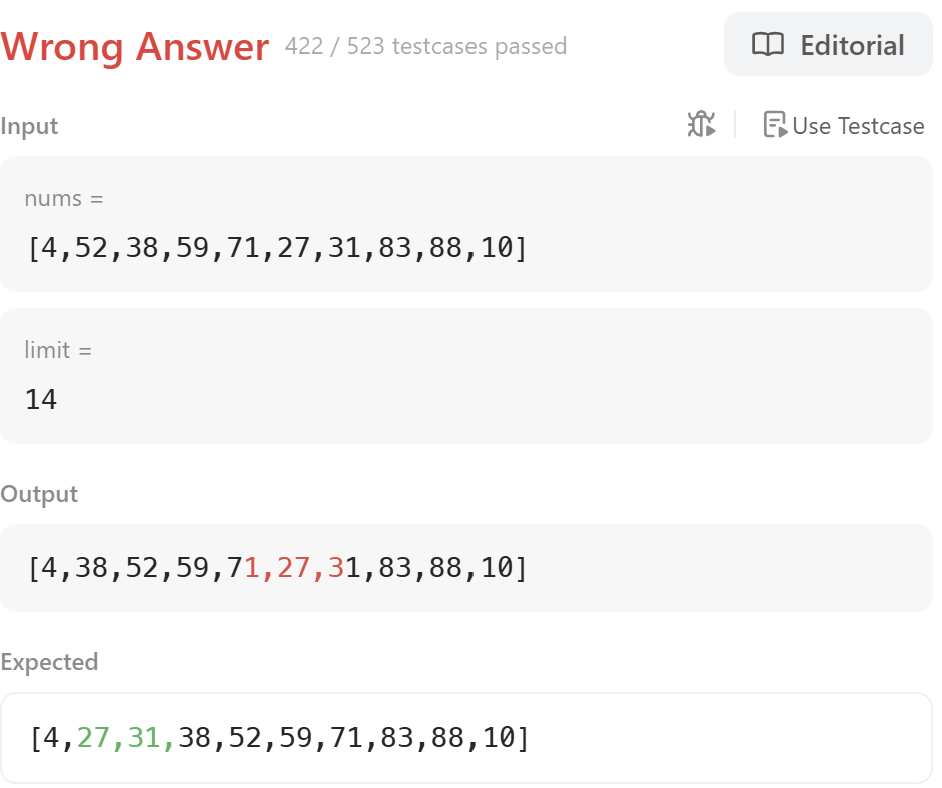
뭔가 코드가 좀 꼬인 기분이 든다.
두 번 째 element에서 52가 38과 swap되고, 그 38은 다시 27과 swap 되지가 않았다.
이를 보완해보자면...
좀 투박하긴 한데 bool type cond를 넣어봤다.
그랬더니 역시나~ time limit 아오!!
class Solution:
def lexicographicallySmallestArray(self, nums: List[int], limit: int) -> List[int]:
n = len(nums)
for i in range(n):
while True:
cond = False
smallest = i
for j in range(i+1,n):
if nums[j] < nums[i] <= nums[j] + limit :
cond = True
if nums[smallest] > nums[j] : smallest = j
nums[i] , nums[smallest] = nums[smallest] , nums[i]
if not cond : break
return nums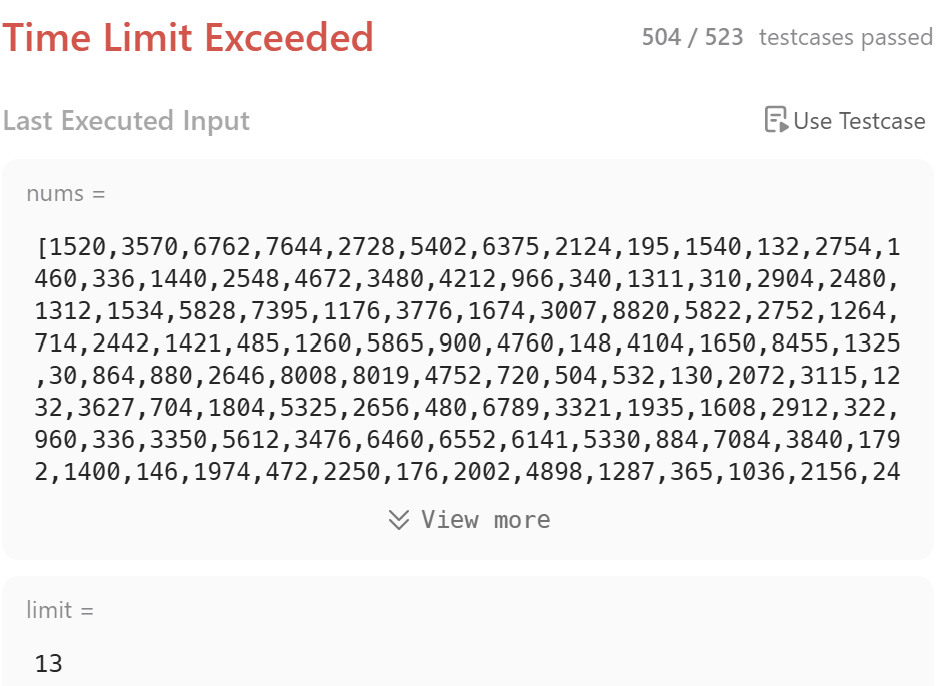
GG...
모범 답안은 아래와 같다.
# 이게 시간 빠른 풀이..
class Solution:
def lexicographicallySmallestArray(self, nums: List[int], limit: int) -> List[int]:
n = len(nums)
# Pair each number with its index and sort by the number
sorted_enum = sorted((num, i) for i, num in enumerate(nums))
new_positions = []
curr_positions = []
prev = float('-inf')
for num, idx in sorted_enum:
# If the current number exceeds the previous number by more than the limit,
# sort and append the current positions to the result
if num > prev + limit:
new_positions.extend(sorted(curr_positions))
curr_positions = [idx]
else:
curr_positions.append(idx)
prev = num
# Append any remaining positions
new_positions.extend(sorted(curr_positions))
# Construct the result array using the new positions
res = [0] * n
for i, idx in enumerate(new_positions):
res[idx] = sorted_enum[i][0]
return res
Union - Find 연습 문제
- LeetCode 684. Redundant Connection
- LeetCode 323. Number of Connected Components in an Undirected Graph
- LeetCode 1319. Number of Operations to Make Network Connected
C++코드는 아래와 같다.
어렵네 참;;
# C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> lexicographicallySmallestArray(vector<int>& nums, int limit) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<int> map;
vector<pair<int, int>> pairs;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
pairs.push_back({nums[i], i});
map.push_back(0);
}
sort(pairs.begin(), pairs.end(), [&](auto& a, auto& b) { return a.first < b.first; });
vector<pair<int, int>> sets = {{n - 1, n - 1}};
for (int i = n - 2, group = 0; i >= 0; --i) {
if (pairs[i + 1].first - pairs[i].first <= limit) {
sets.back().first = i;
map[pairs[i].second] = group;
}
else {
sets.push_back({i, i});
map[pairs[i].second] = ++group;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
nums[i] = pairs[sets[map[i]].first++].first;
}
return nums;
}
};