https://leetcode.com/problems/trapping-rain-water-ii/?envType=daily-question&envId=2025-01-19
Given an m x n integer matrix heightMap representing the height of each unit cell in a 2D elevation map, return the volume of water it can trap after raining.
Example 1:
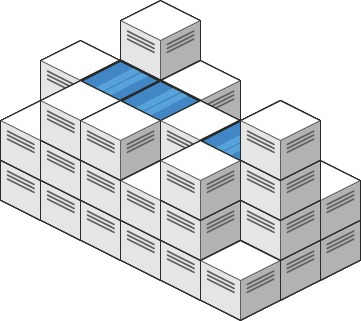
Input: heightMap = [[1,4,3,1,3,2],[3,2,1,3,2,4],[2,3,3,2,3,1]]
Output: 4
Explanation: After the rain, water is trapped between the blocks.
We have two small ponds 1 and 3 units trapped.
The total volume of water trapped is 4.
Example 2:
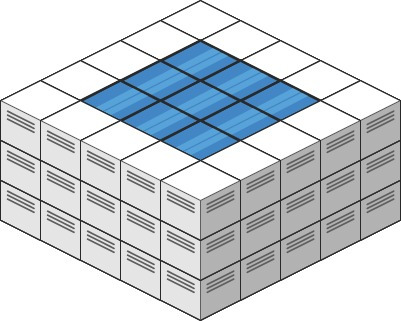
Input: heightMap = [[3,3,3,3,3],[3,2,2,2,3],[3,2,1,2,3],[3,2,2,2,3],[3,3,3,3,3]]
Output: 10
Constraints:
- m == heightMap.length
- n == heightMap[i].length
- 1 <= m, n <= 200
- 0 <= heightMap[i][j] <= 2 * 104
뭔가 극강의 난이도처럼 보이는 Matrix 에서 물 채우기 문제.
사실 이 Water trap 문제는 유명해서 여러 번 마주치긴했는데, 볼 때마다 순수 나의 힘으로만 해결한 적은 없었다.
일단 쫄지 말고 문제에 임해보기
.. 결국 실패
1. Python
Example1, 2 처럼 다 둘러 쌓야있는 건 하겠는데,
테두리 부분에서 물이 새어 나가는 걸 어떻게 구현하는지 못하겠다.
class Solution:
def trapRainWater(self, heightMap: List[List[int]]) -> int:
# m * n Matrix
m = len(heightMap)
n = len(heightMap[0])
def trap1D(water:list[int]) -> int :
l = 0
r = len(water)-1
ans = 0
small = min(water[0],water[r])
while l < r :
if water[l] <= water[r]:
l+=1
if water[l] >= small :
small = water[l]
continue
else : ans += (small-water[l])
else:
r-=1
if water[r] >= small :
small = water[r]
continue
else : ans += (small-water[r])
return ans
curr = 0
for i in range(n):
temp = []
for j in range(m):
temp.append(heightMap[j][i])
curr += trap1D(temp)
return curr
# Nope.. 가생이 edge 부분 처리 X..
흠..
어렵다.. Matrix Direction + heap을 이용하는거네..
# 모범답안
import heapq
from typing import List
class Solution:
def trapRainWater(self, heightMap: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if not heightMap or not heightMap[0]:
return 0
m, n = len(heightMap), len(heightMap[0])
visited = [[False] * n for _ in range(m)]
heap = []
# Step 1: Add all boundary cells to the heap
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if i == 0 or j == 0 or i == m - 1 or j == n - 1:
heapq.heappush(heap, (heightMap[i][j], i, j))
visited[i][j] = True
# Step 2: Process cells in the heap
directions = [(0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1), (-1, 0)]
water_trapped = 0
while heap:
height, x, y = heapq.heappop(heap)
for dx, dy in directions:
nx, ny = x + dx, y + dy
if 0 <= nx < m and 0 <= ny < n and not visited[nx][ny]:
# Calculate trapped water at (nx, ny)
water_trapped += max(0, height - heightMap[nx][ny])
# Update visited cell and push it to the heap
heapq.heappush(heap, (max(height, heightMap[nx][ny]), nx, ny))
visited[nx][ny] = True
return water_trapped
오히려 잘 됐다. 이런 유형의 문제 한 번 다시 복습하고싶었는데,
이 기회에 코드좀 공부해보기
2. C++
# C++
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <tuple>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int trapRainWater(vector<vector<int>>& heightMap) {
int m = heightMap.size(), n = heightMap[0].size();
if (m < 3 || n < 3) return 0;
vector<vector<bool>> visited(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
priority_queue<tuple<int, int, int>, vector<tuple<int, int, int>>, greater<>> minHeap;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i == 0 || i == m - 1 || j == 0 || j == n - 1) {
minHeap.emplace(heightMap[i][j], i, j);
visited[i][j] = true;
}
}
}
int waterTrapped = 0;
vector<int> dirs = {0, 1, 0, -1, 0};
while (!minHeap.empty()) {
auto [height, x, y] = minHeap.top();
minHeap.pop();
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
int nx = x + dirs[d], ny = y + dirs[d + 1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n && !visited[nx][ny]) {
waterTrapped += max(0, height - heightMap[nx][ny]);
minHeap.emplace(max(height, heightMap[nx][ny]), nx, ny);
visited[nx][ny] = true;
}
}
}
return waterTrapped;
}
};'Coding_Practice' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Make Lexicographically Smallest Array by Swapping Elements(Array,Union Find,Sorting) (0) | 2025.01.25 |
|---|---|
| First Completely Painted Row or Column(Array,Hash Table,Matrix) (0) | 2025.01.20 |
| Shifting Letters(Array,String,Prefix Sum) (0) | 2025.01.16 |
| Number of Music Playlists(Math,Dynamic Programming,Combinatorics) (0) | 2025.01.16 |
| Uncrossed Lines(Array,Dynamic Programming) (0) | 2025.01.15 |