https://leetcode.com/problems/delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array/description/
You are given an array of integers nums and the head of a linked list. Return the head of the modified linked list after removing all nodes from the linked list that have a value that exists in nums.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3], head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [4,5]
Explanation:
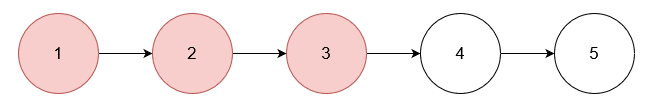
Remove the nodes with values 1, 2, and 3.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1], head = [1,2,1,2,1,2]
Output: [2,2,2]
Explanation:
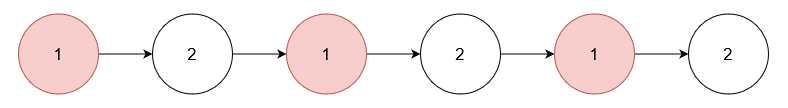
Remove the nodes with value 1.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [5], head = [1,2,3,4]
Output: [1,2,3,4]
Explanation:
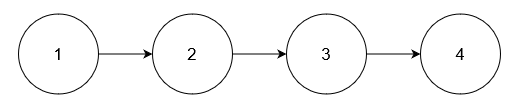
No node has value 5.
Constraints:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 105
- 1 <= nums[i] <= 105
- All elements in nums are unique.
- The number of nodes in the given list is in the range [1, 105].
- 1 <= Node.val <= 105
- The input is generated such that there is at least one node in the linked list that has a value not present in nums
1. C++
그냥 일반적으로 if(find(nums.begin(),nums.end(),curr->val) != nums.end()) 을 쓸 때는 time이 너무 오래걸린다고 뜬다..
|
The primary issue with your code is the use of the find() function inside the loop, which has a time complexity of O(n)O(n) for each call. Since you're calling find() for each node in the linked list, this results in a total time complexity of O(m×n)O(m \times n), where mm is the number of elements in nums and nn is the number of nodes in the linked list. This can lead to a time limit exceeded (TLE) error for larger inputs.
Optimized ApproachTo optimize this, you can improve the lookup of nums by using a std::unordered_set, which provides O(1)O(1) average time complexity for lookups, significantly reducing the time complexity of the solution to O(m+n)O(m + n), where mm is the size of nums and nn is the number of nodes in the linked list. |
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {
if(!head) return head;
ListNode* curr = head;
ListNode* prev = nullptr;
int cnt = 0;
unordered_set<int> numSet(nums.begin(), nums.end());
while(curr){
if(numSet.find(curr->val)!=numSet.end()){//find it
curr=curr->next;
if(prev) prev->next = curr; // check prev->nullptr
}else{ //not find it in nums
cnt++;
prev=curr;
curr=curr->next;
}
if(cnt==1) head = prev;
}
if(cnt==0) head=nullptr;
return head;
}
};
2. Python
Hashing을 제대로 하기 위해선 일단 data들을 set에 저장해두어야 속도가 빠르다.
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def modifiedList(self, nums: List[int], head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
num_set = set(nums)
dummy = ListNode(-999)
curr = head
prev = dummy
while curr :
prev.next = curr
if curr.val in num_set :
curr = curr.next
else:
prev = curr
curr = curr.next
prev.next = curr
return dummy.next
근데 이게 솔직히 while문 안쪽이 번잡스럽다..
좀 깔끔하게 다시 적으면 아래와 같음
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def modifiedList(self, nums: List[int], head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
num_set = set(nums)
dummy = ListNode(-999)
dummy.next = head # for the case staring with OK data
curr = head
prev = dummy
while curr :
if curr.val in num_set :
prev.next = curr.next
else:
prev = curr
curr = curr.next
return dummy.next
즉, dummy Node는 사실상 초장부터 remove data가 나올 때를 대비한 것이다.