https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/
Given the head of a singly linked list, reverse the list, and return the reversed list.
Example 1:
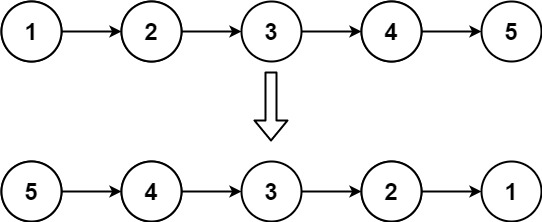
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [5,4,3,2,1]
Example 2:
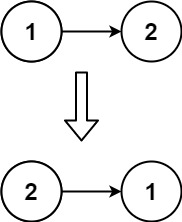
Input: head = [1,2]
Output: [2,1]
Example 3:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is the range [0, 5000].
- -5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
Follow up: A linked list can be reversed either iteratively or recursively. Could you implement both?
1. Python
- iteratively 푼 것
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head : return head
p = None
curr = head
n = curr.next
while n :
curr.next = p
p = curr
curr = n
n = curr.next
curr.next = p
return currnext를 따로 만들어 줄 필요도 없었다;;
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head : return None
curr = head
prev = None
while curr:
temp = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = temp
return prev
- Recursive 하게도 고고
모르겠어서 답지 참고..
언제봐도 Recursion은 진짜 신의 경지다. 뇌꼬인다 뇌 꼬여 ㅠ
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head or not head.next : return head
new_head = self.reverseList(head.next)
head.next.next = head
head.next = None
return new_headRecursive를 볼때마다 인성이 파탄나는듯 하다..
2. C
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
if(!head) return NULL;
struct ListNode* prev = NULL;
struct ListNode* curr = head;
while(curr){
struct ListNode* temp = curr->next;
curr->next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = temp;
}
return prev;
}
3. C++
얘는 Recursive하게..
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head||!(head->next)) return head;
ListNode* new_node = reverseList(head->next);
head -> next -> next = head;
head -> next = NULL;
return new_node;
}
};
경이로운 코딩의 세계..
'Coding_Practice' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Convert 1D Array Into 2D Array[E,Array,Matrix,Simulation] (0) | 2024.07.26 |
|---|---|
| Adding Spaces to a String[M,ArrayTwo Pointers,String,Simulation] (0) | 2024.07.26 |
| Design HashMap[E,Array,Hash Table,Linked List,Design,Hash Function] (2) | 2024.07.26 |
| Design Circular Deque[M,Array,Linked List,Design,Queue] (0) | 2024.07.26 |
| Linked List Cycle(E,Hash Table,Linked List,Two Pointers) (0) | 2024.07.26 |