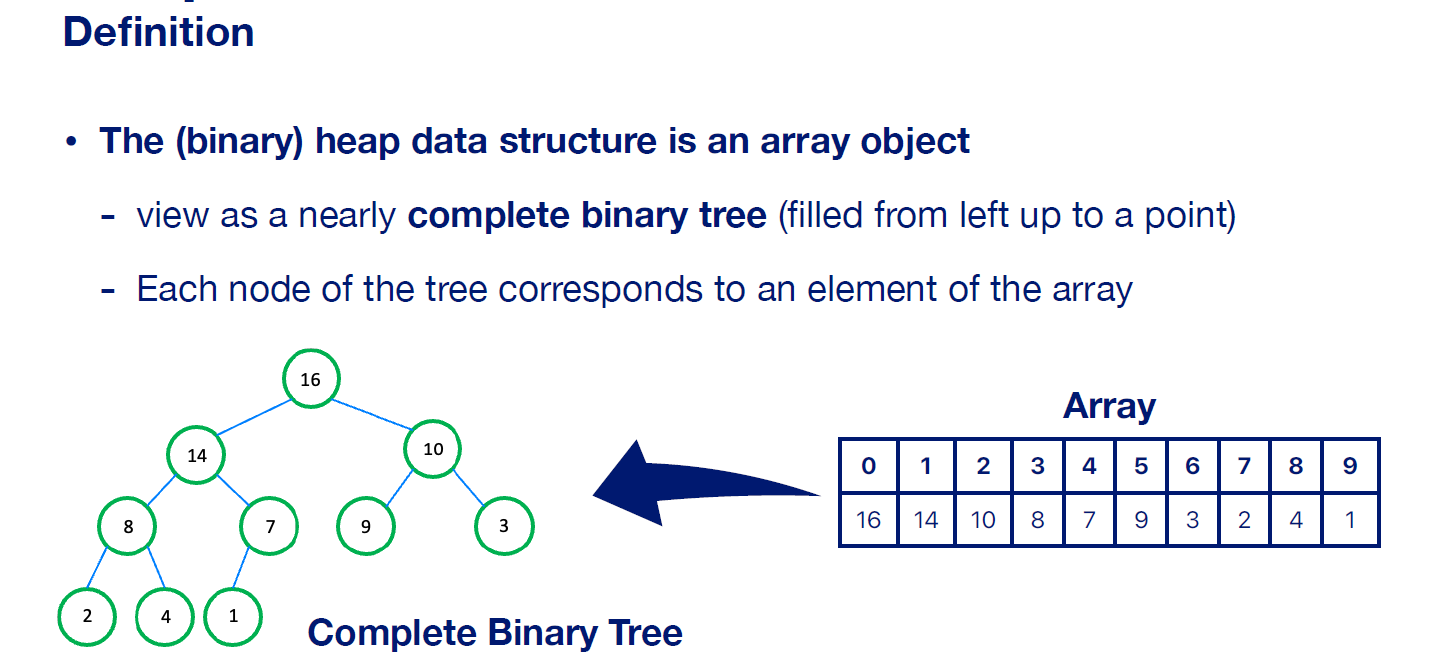
Python / C / C++에서 Array / Linked List 기반으로 heap 구조를 만들어보겠다.
Skeleton Code는 GPT를 참고했으며, Min/Max heap은 사실 한 끝 차이라 이 둘을 그냥 번갈아가면서 구현해보기로 한다.
1. Python - Array - Min heap
class PriorityQueueArray:
def __init__(self, is_min=True):
self.heap = []
self.is_min = is_min # True for min-heap, False for max-heap
def parent(self, i):
return (i - 1) // 2
def left_child(self, i):
return 2 * i + 1
def right_child(self, i):
return 2 * i + 2
def enqueue(self, key):
# TODO: Add element and maintain heap property
self.heap.append(key)
n = len(self.heap)-1
#bubble up
while n != 0 and self.heap[self.parent(n)] > self.heap[n]:
self.heap[self.parent(n)],self.heap[n] = self.heap[n],self.heap[self.parent(n)]
n = self.parent(n)
def dequeue(self):
# TODO: Remove and return top element while maintaining heap property
temp = self.heap[0]
n = len(self.heap)
self.heap[0],self.heap[n-1] = self.heap[n-1],self.heap[0]
self.heap.pop()
self.heapify(0)
return temp
def heapify(self, i):
# TODO: Maintain heap property at index i
# min-heap
if self.is_min:
smallest = i
left = self.left_child(i)
right = self.right_child(i)
if left<len(self.heap) and self.heap[i] > self.heap[left]:
smallest = left
if right<len(self.heap) and self.heap[smallest] > self.heap[right]:
smallest = right
if smallest != i:
self.heap[i],self.heap[smallest] = self.heap[smallest],self.heap[i]
self.heapify(smallest)
# max는 else 후 반대로
def print_queue(self):
print(self.heap)
# Test case
pq = PriorityQueueArray(is_min=True)
pq.enqueue(10)
pq.enqueue(5)
pq.enqueue(20)
pq.enqueue(1)
pq.print_queue()
print(pq.dequeue())
pq.print_queue()
[1, 5, 20, 10]
1
[5, 10, 20]
2. Python - Linked-list - Max heap
# Max heap
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.key = key
self.next = None
class PriorityQueueLinkedList:
def __init__(self, is_min=True):
self.head = None
self.is_min = is_min # True for min-priority, False for max-priority
def enqueue(self, key):
# TODO: Add element while maintaining priority order
new_node = Node(key)
if not self.head:
self.head = new_node
return
else:
curr = self.head
if curr.key < new_node.key:
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
else:
while curr.next and curr.next.key > new_node.key :
curr = curr.next
new_node.next = curr.next
curr.next = new_node
"""
--> enqueue 부분 이렇게 깔끔하게 수정 가능
def enqueue(self, key):
# TODO: Add element while maintaining priority order
new_node = Node(key)
curr = self.head
if not self.head or self.head.key < new_node.key:
new_node.next= self.head
self.head = new_node
else:
while curr.next and curr.next.key > new_node.key :
curr = curr.next
new_node.next = curr.next
curr.next = new_node
"""
def dequeue(self):
# TODO: Remove and return the highest/lowest priority element
if not self.head : return
else:
temp = self.head.key
self.head = self.head.next
return temp
def print_queue(self):
current = self.head
while current:
print(current.key, end=" -> ")
current = current.next
print("None")
# Test case
pq = PriorityQueueLinkedList(is_min=False)
pq.enqueue(10)
pq.enqueue(5)
pq.enqueue(20)
pq.enqueue(1)
pq.print_queue()
print(pq.dequeue())
pq.print_queue()
20 -> 10 -> 5 -> 1 -> None
20
10 -> 5 -> 1 -> None
3. C - Array - Max heap
Size에 따른 index 접근은 method 내에서 통일시켜 구현하자.
ex) size-1 / size 이런식으로 같은 걸 분리해서 계산하면 뭔가 어디서 꼬인다.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
typedef struct {
int data[MAX_SIZE]; // Array to store heap elements
int size; // Current number of elements in the heap
} MaxHeapArray;
// Function prototypes
void swap(int* a, int* b){
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
void init_heap(MaxHeapArray* heap);
void insert(MaxHeapArray* heap, int key);
int extract_max(MaxHeapArray* heap);
void heapify(MaxHeapArray* heap, int index);
void print_heap(MaxHeapArray* heap);
// Function definitions (to be implemented)
void init_heap(MaxHeapArray* heap) {
// TODO: Initialize the heap structure
heap->size = 0;
}
void insert(MaxHeapArray* heap, int key) {
// TODO: Add an element to the heap and restore max-heap property
heap->data[heap->size] = key;
heap->size++;
for(int i=heap->size-1;i>=0;i--){
heapify(heap,i);
}
}
int extract_max(MaxHeapArray* heap) {
// TODO: Remove and return the maximum element (root)
if(heap->size == 0) return -1;
else{
int ans = heap->data[0];
heap->data[0] = heap->data[heap->size-1];
// heap->data[heap->size-1] = NULL;
heap->size--;
heapify(heap,0);
return ans;
}
}
void heapify(MaxHeapArray* heap, int index) {
// TODO: Restore max-heap property from the given index
int largest = index;
int left = index*2+1;
int right = index*2+2;
int n = heap->size;
if(left < n && heap->data[left] > heap->data[index]) largest = left;
if(right < n && heap->data[right] > heap->data[largest]) largest = right;
if(largest != index){
swap(&(heap->data[index]),&(heap->data[largest]));
heapify(heap,largest);
}
}
void print_heap(MaxHeapArray* heap) {
// TODO: Print the elements of the heap
for(int i=0;i<heap->size;i++){
printf("%d ",heap->data[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// Main function to test the logic
int main() {
MaxHeapArray heap;
init_heap(&heap);
// Test cases
insert(&heap, 10);
insert(&heap, 5);
insert(&heap, 20);
insert(&heap, 1);
insert(&heap, 7);
insert(&heap, 11);
insert(&heap, 30);
printf("Heap after insertions: ");
print_heap(&heap);
printf("Extracted Max: %d\n", extract_max(&heap));
printf("Heap after extraction: ");
print_heap(&heap);
return 0;
}
4. C / Linked - list / Min heap
// C - Minheap
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
} Node;
typedef struct {
Node* head; // Points to the head of the list
} MaxHeapLinkedList;
// Initialize the heap
void init_heap(MaxHeapLinkedList* heap) {
heap->head = NULL;
}
// Print the heap elements
void print_heap(MaxHeapLinkedList* heap) {
Node* current = heap->head;
while (current) {
printf("%d -> ", current->key);
current = current->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
// Function definitions (to be implemented)
void insert(MaxHeapLinkedList* heap, int key) {
// TODO: Add an element to the linked list while maintaining min-heap property
Node* new_node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
new_node -> key = key;
new_node -> next = NULL;
if(!heap->head || heap->head->key > new_node -> key){
new_node -> next = heap->head;
heap->head = new_node;
}else{
Node* temp = heap->head;
while(temp->next && temp->next->key < new_node->key){
temp = temp->next;
}
new_node->next = temp->next;
temp->next = new_node;
}
}
int extract_min(MaxHeapLinkedList* heap) {
// TODO: Remove and return the maximum element
if(!heap->head){
printf("ERROR\n");
return -1;
}
else{
int ans = heap->head->key;
Node* temp = heap->head;
heap->head = heap->head->next;
free(temp);
return ans;
}
}
// Main function to test the logic
int main() {
MaxHeapLinkedList heap;
init_heap(&heap);
// Test cases
insert(&heap, 10);
insert(&heap, 5);
insert(&heap, 20);
insert(&heap, 7);
insert(&heap, 11);
insert(&heap, 999);
insert(&heap, 1);
printf("Heap after insertions: ");
print_heap(&heap);
printf("Extracted Min: %d\n", extract_min(&heap));
printf("Heap after extraction: ");
print_heap(&heap);
printf("Extracted Min: %d\n", extract_min(&heap));
printf("Heap after extraction: ");
print_heap(&heap);
insert(&heap, 0);
insert(&heap, 3);
printf("Heap after insertions: ");
print_heap(&heap);
return 0;
}
Heap after insertions: 1 -> 5 -> 7 -> 10 -> 11 -> 20 -> 999 -> NULL
Extracted Min: 1
Heap after extraction: 5 -> 7 -> 10 -> 11 -> 20 -> 999 -> NULL
Extracted Min: 5
Heap after extraction: 7 -> 10 -> 11 -> 20 -> 999 -> NULL
Heap after insertions: 0 -> 3 -> 7 -> 10 -> 11 -> 20 -> 999 -> NULL
C++의 경우, 이번엔 Array 에서 Min heap 구조를 만들어 보겠다.
linked list의 경우 sentinel node를 이용해보는 것으로!
좀 어정쩡하긴 한데,
heap의 size의 경우 그냥 heap.size()로 관리해도 무방하다.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class MinHeapArray {
private:
vector<int> heap;
int size;
void heapify(int index);
int parent(int i){return (i-1)/2;}
int left(int i){return i*2+1;}
int right(int i){return i*2+2;}
public:
MinHeapArray() {size = 0;}
void insert(int key);
int extract_min();
void print_heap() const;
};
// Initialize the heap
void MinHeapArray::print_heap() const {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
cout << heap[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
// Function definitions (to be implemented)
void MinHeapArray::insert(int key) {
// TODO: Add an element to the heap and restore min-heap property
heap.push_back(key);
size++;
int n = size-1;
// Bubble up
while(n>0 && heap[parent(n)] > heap[n]){
swap(heap[parent(n)],heap[n]);
n = parent(n);
}
}
int MinHeapArray::extract_min() {
// TODO: Remove and return the minimum element (root) while maintaining the heap property
if(size==0){
cout << "ERROR" << endl;
return -1;
}else{
int ans = heap[0];
swap(heap[0],heap[size-1]);
heap.pop_back();
size--;
// for(int i=size/2;i>=0;i--){ // 반만 돌아도 heapify 만족가능 --> children 없는 Node들 무시
// heapify(i);
// }
heapify(0);
return ans;
}
}
void MinHeapArray::heapify(int index) {
// TODO: Restore the min-heap property after deletion
int smallest = index;
int l = left(index);
int r = right(index);
if(l<size && heap[l] < heap[index]) smallest = l;
if(r<size && heap[r] < heap[smallest]) smallest = r;
if(smallest != index){
swap(heap[index],heap[smallest]);
heapify(smallest);
}
}
// Main function to test the logic
int main() {
MinHeapArray heap;
// Test cases
heap.insert(10);
heap.insert(5);
heap.insert(20);
heap.insert(7);
heap.insert(11);
heap.insert(999);
heap.insert(1);
cout << "Heap after insertions: ";
heap.print_heap();
cout << "Extracted Min: " << heap.extract_min() << endl;
cout << "Heap after extraction: ";
heap.print_heap();
cout << "Extracted Min: " << heap.extract_min() << endl;
cout << "Heap after extraction: ";
heap.print_heap();
heap.insert(0);
heap.insert(3);
cout << "Heap after insertions: ";
heap.print_heap();
return 0;
}
Heap after insertions: 1 7 5 10 11 999 20
Extracted Min: 1
Heap after extraction: 5 7 20 10 11 999
Extracted Min: 5
Heap after extraction: 7 10 20 999 11
Heap after insertions: 0 10 3 999 11 20 7
이제는,
마지막으로 Max heap을 C++ linked list + Sentinel Node로 만들어보기
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Node structure for Linked List
struct Node {
int key;
Node* next;
Node(int k) : key(k), next(nullptr) {}
};
// MaxHeap implemented using Linked List with a Sentinel Node
class MaxHeapLinkedList {
private:
Node* sentinel; // Sentinel node to simplify boundary conditions
public:
// Constructor
MaxHeapLinkedList() {
sentinel = new Node(-1); // Sentinel node with dummy key
sentinel->next = nullptr;
}
// Destructor to clean up memory
~MaxHeapLinkedList() {
Node* current = sentinel;
while (current) {
Node* temp = current;
current = current->next;
delete temp;
}
}
// Initialize the heap (reset)
void init_heap() {
Node* current = sentinel->next;
while (current) {
Node* temp = current;
current = current->next;
delete temp;
}
sentinel->next = nullptr;
}
// Insert a new key into the heap
void insert(int key);
// Extract the maximum key from the heap
int extract_max();
// Print the heap elements
void print_heap() const {
Node* current = sentinel->next; // Skip the sentinel node
while (current) {
cout << current->key << " -> ";
current = current->next;
}
cout << "NULL" << endl;
}
};
// Main function to test the logic
int main() {
MaxHeapLinkedList heap;
// Initialize the heap
heap.init_heap();
// Test cases
heap.extract_max(); // ERROR
heap.insert(10);
heap.insert(5);
heap.insert(20);
heap.insert(7);
heap.insert(11);
cout << "Heap after insertions: ";
heap.print_heap();
cout << "Extracted Max: " << heap.extract_max() << endl;
cout << "Heap after extraction: ";
heap.print_heap();
cout << "Extracted Max: " << heap.extract_max() << endl;
cout << "Heap after extraction: ";
heap.print_heap();
heap.insert(15);
cout << "Heap after insertions: ";
heap.print_heap();
return 0;
}
// Function definitions (to be implemented)
void MaxHeapLinkedList::insert(int key) {
// TODO: Insert a new key into the list while maintaining max-heap property
// Implement by finding the correct position in descending order
Node* temp = sentinel;
Node* new_node = new Node(key);
while(temp->next && temp->next->key > new_node->key){
temp = temp->next;
}
new_node -> next = temp -> next;
temp -> next = new_node;
}
int MaxHeapLinkedList::extract_max() {
// TODO: Remove and return the maximum key while maintaining max-heap property
// Remove the first node after the sentinel and re-adjust the list
if(!sentinel->next){
cout << "ERROR\n"<<endl;
return -1;
}
else{
int ans = sentinel->next->key;
Node* temp = sentinel->next;
sentinel->next = sentinel->next->next;
delete temp;
return ans;
}
}
ERROR
Heap after insertions: 20 -> 11 -> 10 -> 7 -> 5 -> NULL
Extracted Max: 20
Heap after extraction: 11 -> 10 -> 7 -> 5 -> NULL
Extracted Max: 11
Heap after extraction: 10 -> 7 -> 5 -> NULL
Heap after insertions: 15 -> 10 -> 7 -> 5 -> NULL
요기까지..~~~
위 self - study에 사용했던 코드는 아래에 첨부한다.
'SW 만학도 > C' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Linked list with Stack Node 문제 (0) | 2024.12.23 |
|---|---|
| C Struct 연습 (0) | 2024.08.22 |
| C programming file I/O 연습 (0) | 2024.08.21 |
| Review 6 - Linked list in C (0) | 2024.07.10 |
| Review 5 - Dynamic(Structure) in C (0) | 2024.07.08 |