https://leetcode.com/problems/symmetric-tree/description/
Given the root of a binary tree, check whether it is a mirror of itself (i.e., symmetric around its center).
Example 1:
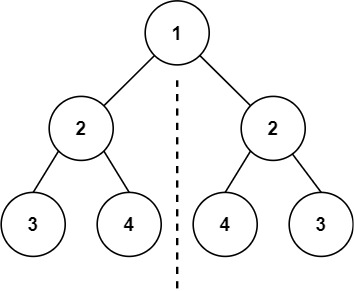
Input: root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3]
Output: true
Example 2:

Input: root = [1,2,2,null,3,null,3]
Output: false
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 1000].
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Could you solve it both recursively and iteratively?
아 진짜 너무 짜증난다.
분명 recursive / iterative 두 가지 방식으로 풀어봤던 문제인데 도저히 풀이법이 생각이 안 난다.
돌머리가 된 것이 분명하다.
1. Python
- Iterative: 생각해보면 또 간단한건데.. 돌아버리겠네~~
왜 이리 기억이 안 나냐!!
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isSymmetric(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
if not root : return True
q = deque([(root.left,root.right)])
while q:
left, right = q.popleft()
if not left and not right:
continue
if not left or not right:
return False
if left.val != right.val:
return False
q.append((left.left,right.right));
q.append((left.right,right.left));
return True
- Recursive:
쉬운게 하나 없고,
Master 한다는 개념은 없다!
끊임 없이 진전해야 한다..
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isSymmetric(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
if not root : return True
if not root.left and not root.right : return True
def help(node_l,node_r:TreeNode):
if not node_l and not node_r : return True
if not node_l or not node_r : return False
if node_l.val != node_r.val : return False
return help(node_l.left,node_r.right) and help(node_l.right,node_r.left)
return help(root.left,root.right)
2. C
C에선 queue가 없어서 도저히 Container를 통한 iteration이 되지 않는다.
그래서 그냥 Recursive만 해보기로 한다.
- iterative [ GPT ver ]
되긴 하는데,, 좀 무식하다 상당히 ㅠ .. 일차원적이고,,
if (!root) return 1;
// Initialize two arrays to store nodes at each level
struct TreeNode* leftQueue[10000];
struct TreeNode* rightQueue[10000];
int leftFront = 0, leftRear = 0;
int rightFront = 0, rightRear = 0;
// Start with the root's left and right children
leftQueue[leftRear++] = root->left;
rightQueue[rightRear++] = root->right;
while (leftFront < leftRear && rightFront < rightRear) {
struct TreeNode* leftNode = leftQueue[leftFront++];
struct TreeNode* rightNode = rightQueue[rightFront++];
if (!leftNode && !rightNode) continue;
if (!leftNode || !rightNode) return 0;
if (leftNode->val != rightNode->val) return 0;
// Enqueue children in reverse order for comparison
leftQueue[leftRear++] = leftNode->left;
leftQueue[leftRear++] = leftNode->right;
rightQueue[rightRear++] = rightNode->right;
rightQueue[rightRear++] = rightNode->left;
}
return 1;
- Recursive
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
bool help(struct TreeNode* left,struct TreeNode* right){
if(!left && !right) return 1;
if(!left || !right) return 0;
return (left->val == right->val)&&help(left->left,right->right)&&help(left->right,right->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) return 1;
return help(root->left,root->right);
}
3. C++
- Iteratively
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
//Recursive
if(!root) return true;
queue<pair<TreeNode*,TreeNode*>> q;
q.push({root->left,root->right});
while(!q.empty()){
TreeNode* l = q.front().first;
TreeNode* r = q.front().second;
q.pop();
if(!l && !r) continue;
if(!l || !r) return false;
if(l->val != r->val) return false;
q.push({l->left,r->right});
q.push({l->right,r->left});
}
return true;
}
};
- Recursively
코드 참 짧고 예쁘다.
담음새가 좋은 요리같다.
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool help(TreeNode* left,TreeNode* right){
if(!left && !right) return true;
if(!left || !right) return false;
return (left->val==right->val) && help(left->left,right->right) && help(left->right,right->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
//Recursive
if(!root) return true;
return help(root->left,root->right);
}
};'Coding_Practice' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Combination Sum - Back Tracking (Python) (0) | 2024.08.02 |
|---|---|
| Linked List Loops(Python) (0) | 2024.08.02 |
| Maximum Level Sum of a Binary Tree[M,Tree,Depth-First Search,Breadth-First Search,Binary Tree] (0) | 2024.07.31 |
| Binary Tree Inorder Traversal[E,Stack,Tree,Depth-First Search,Binary Tree] (0) | 2024.07.31 |
| C++ Container, Custom Map Practice (0) | 2024.07.29 |