https://leetcode.com/problems/n-ary-tree-level-order-traversal/description/
Given an n-ary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes' values.
Nary-Tree input serialization is represented in their level order traversal, each group of children is separated by the null value (See examples).
Example 1:
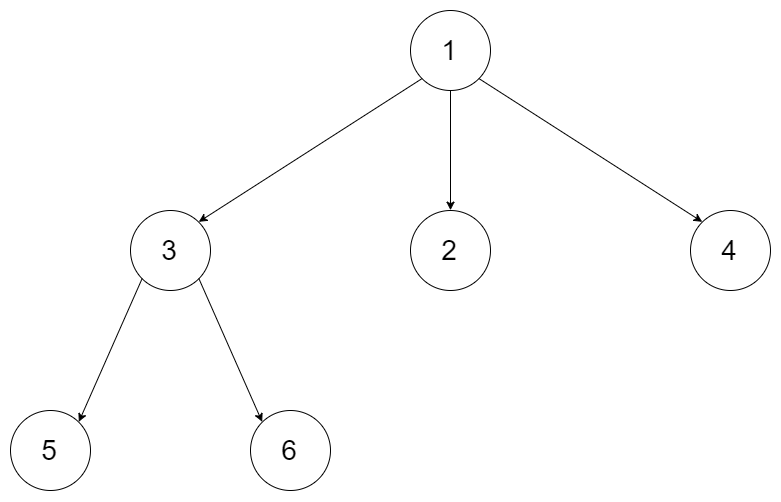
Input: root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
Output: [[1],[3,2,4],[5,6]]
Example 2:
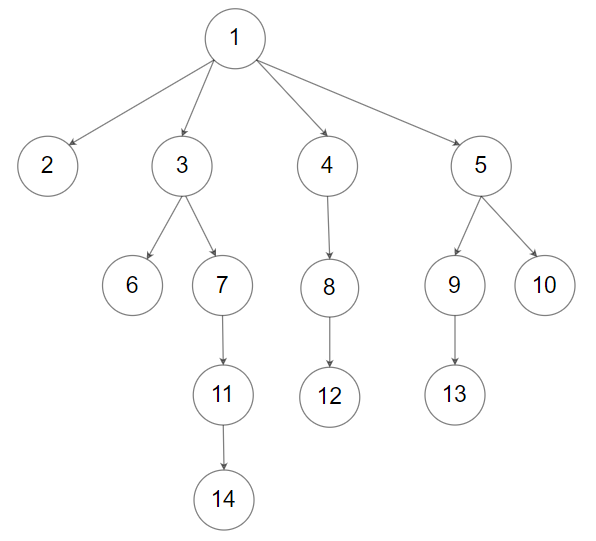
Input: root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
Output: [[1],[2,3,4,5],[6,7,8,9,10],[11,12,13],[14]]
Constraints:
- The height of the n-ary tree is less than or equal to 1000
- The total number of nodes is between [0, 104]
아 역시 M(Medium) 난이도는 틀만 봐도 난해하다..
1. Python
도저히 문제 이해가 안 가서 gg
구냥 BFS를 구현하면 됐다. 근데 이게 답을 보고나면 쉬워보이는데 첨엔 똥볼좀 찼다..
쟁점은 children attribute가 사실 node의 children을 다 포함하고 있는 container였던 것..
나는 괜히 null로 children 구분해야하나..? 하고 쫄았네
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution:
def levelOrder(self, root: 'Node') -> List[List[int]]:
if not root : return []
ans = []
q = deque([root])
while q:
lv_size = len(q)
lv_node = []
for x in range(lv_size):
node = q.popleft()
lv_node.append(node.val)
for child in node.children:
q.append(child)
ans.append(lv_node)
return ans
2. C
gg 더블포인터 뭐냐 도대체
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/**
* Definition for a Node.
* struct Node {
* int val;
* int numChildren;
* struct Node** children;
* };
*/
/**
* Return an array of arrays of size *returnSize.
* The sizes of the arrays are returned as *returnColumnSizes array.
* Note: Both returned array and *columnSizes array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int** levelOrder(struct Node* root, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes) {
if (!root) {
*returnSize = 0;
*returnColumnSizes = NULL;
return NULL;
}
// 최대 레벨 수를 1000으로 가정
int** result = (int**)malloc(1000 * sizeof(int*));
*returnColumnSizes = (int*)malloc(1000 * sizeof(int));
*returnSize = 0;
// 큐의 최대 크기를 10000으로 가정
struct Node** queue = (struct Node**)malloc(10000 * sizeof(struct Node*));
int front = 0, rear = 0;
queue[rear++] = root;
while (front < rear) {
int levelSize = rear - front;
result[*returnSize] = (int*)malloc(levelSize * sizeof(int));
(*returnColumnSizes)[*returnSize] = levelSize;
for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {
struct Node* node = queue[front++];
result[*returnSize][i] = node->val;
for (int j = 0; j < node->numChildren; j++) {
queue[rear++] = node->children[j];
}
}
(*returnSize)++;
}
free(queue);
return result;
}선을 넘어버리는 C코드;;
죄악이다 진짜
3. C++
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
// Node 구조체 정의
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
if (!root) {
return result;
}
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
int levelSize = q.size();
vector<int> levelNodes;
for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; ++i) {
Node* node = q.front();
q.pop();
levelNodes.push_back(node->val);
for (Node* child : node->children) {
q.push(child);
}
}
result.push_back(levelNodes);
}
return result;
}
};'Coding_Practice' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Linked List Cycle(E,Hash Table,Linked List,Two Pointers) (0) | 2024.07.26 |
|---|---|
| Removing Minimum Number of Magic Beans[M,Array,Greedy,Sorting,Enumeration,Prefix Sum] (0) | 2024.07.26 |
| Semi-Ordered Permutation[E,Array,Simulation] (4) | 2024.07.24 |
| Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays[M,Array,Dynamic Programming] (1) | 2024.07.24 |
| Largest Odd Number in String[E,Math,String,Greedy] (4) | 2024.07.23 |